Dr.patel
what are urinary casts?
Urinary casts refers to cylindrical or tube-like structures found in the urine upon microscopic examination.These casts are composed of various substances, including proteins, cells, cellular debris, and other materials that are present within the renal tubules.
Casts are the only formed elements in urine that have kidney as their sole site of origin .Tamm-Horsfall protein ( also known as uromodulin) is the glycoprotein secreted by renal tubules which constitutes one third of the total urinary protein in normal individual. Tamm-Horsfall protein forms matrix of all casts ,the protein form meshwork of fibrils that trap any elements present in tubular filtrate, including cells, cell fragments ,pigment, granular material. The microscopic examination of urinary sediments plays a crucial role in assessing kidney function and identifying various renal conditions.
Types of urinary casts
Hyaline casts are primarily composed of Tamm-Horsfall protein, which is exclusively synthesized by the renal tubular epithelial cells in the kidney.
Under normal conditions, small numbers(0 – 2/low power field )are normal of hyaline casts can be observed in urine samples. Under microscope these appear transparent, colorless acellular, homogenous matrix and Smooth surface with rounded ends .
clinical significance of hyaline cast: Frequently seen in individuals post-exercise or with dehydration and fever.They also can accompany other casts in pathologic conditions.

Granular casts: Contains fine or coarse granules derived from degenerated cellular debris or precipitated protein. . Granular casts have coarse and fine granules in the cast matrix. Often appears “muddy brown”
clinical significance: Granular casts are seen in both pathologic and non-pathologic conditions. Often they can be seen in conjunction with hyaline casts following strenuous exercise.usually accompanied with proteinuria in glomerular pathology

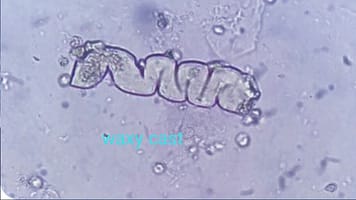
Waxy casts : These casts appear broad, highly refractive casts with smooth or may have jagged edges and notches. They indicate stasis or stenosis within the renal tubules and are associated with chronic renal failure.
clinical significance of waxy casts: seen in
- Tubular inflammation and degeneration
- Chronic renal failure
- Acute and chronic renal allograft rejection
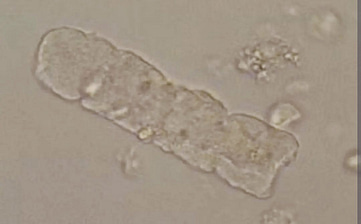
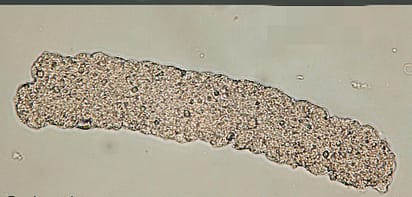
Broad casts : These are wider than other casts and often contain cellular debris. Diameter is 2-6 times that of the regular cast.The term “broad” is added to the type of cast observed
clinical significance of broad casts Their presence suggests severe tubular injury or chronic end stage renal disease,extreme urine stasis.
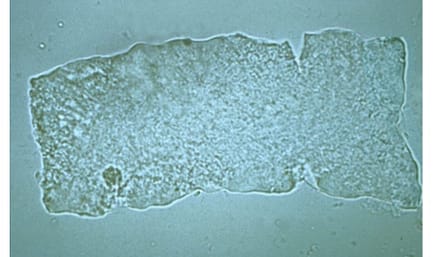
Red Blood Cell Casts or RBC cast :
These appear orange-red color. They have a more irregular shape as a result of tightly packed RBCs adhering to the protein matrix. look for free RBC and strip finding to differentiate RBC cast from other cast
clinical significance of RBC casts:They are commonly associated with glomerulonephritis or vasculitis.
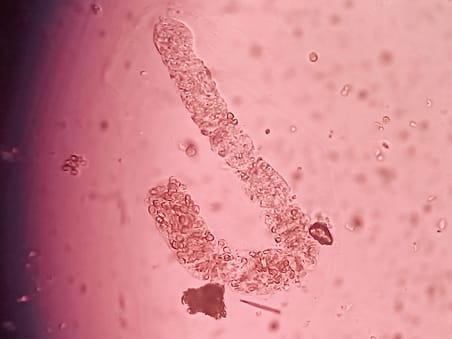
White Blood Cell Casts (WBC casts): Protein matrix variably filled with WBCs can be intact or disintegrating WBCs in the matrix. Can be differentiated from WBC clumps by observing cylindrical shape and cast matrix. Mainly composed of neutrophils.
clinical significance of WBC casts in urine:Seen in pyelonephritis but can indicate other causes of tubulointerstitial inflammation.
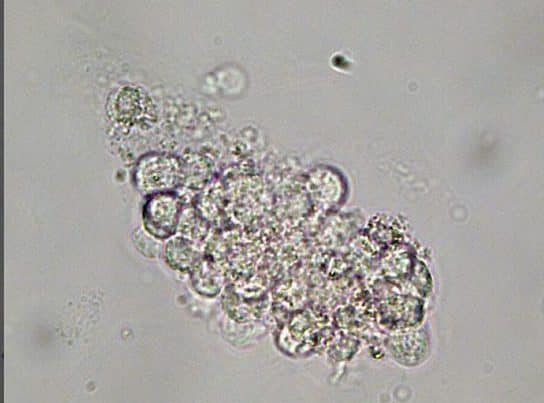
WBC cast
Epithelial cell cast:Epithelial casts contain renal tubular epithelial cells that have been shed from damaged tubules. Staining and the use of phase microscopy can be used to identify the nuclear detail.
Clinical significance of Epithelial cell casts: Seen in Renal tubular damage,Acute tubular necrosis,Acute allograft rejection, Nephrotic syndrome,lupus nephritis
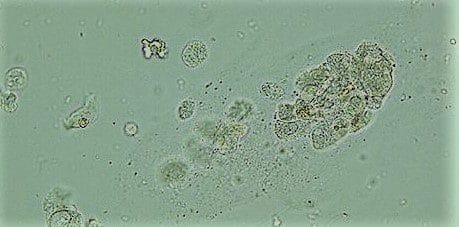
Renal Epithelial cell casts
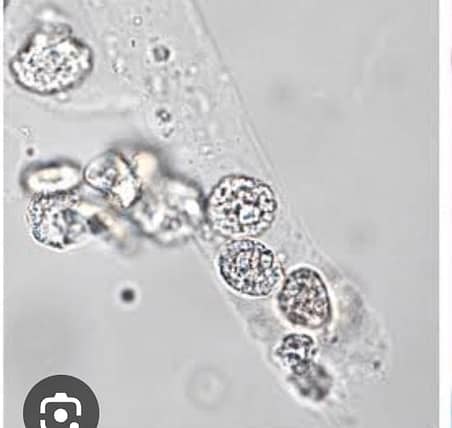
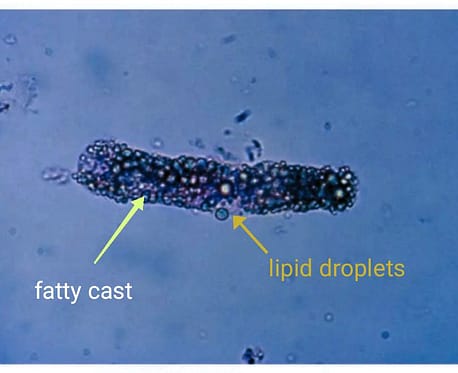
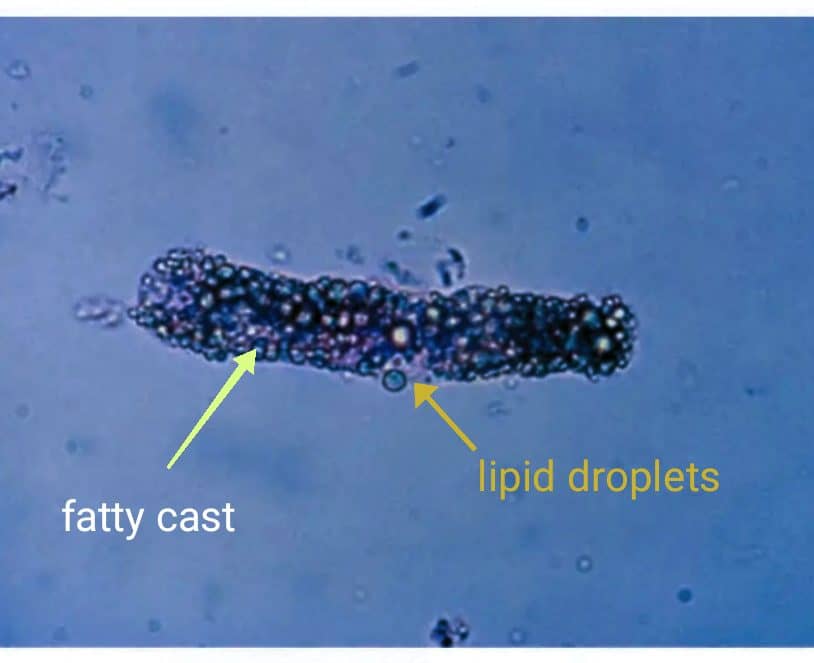
Fatty casts: Fatty casts contain highly refractile fat globules and are seen in conditions such as nephrotic syndrome, where there is altered lipid metabolism. staining with Sudan III or examining under polarized light for the presence of Maltese-cross formation heps in verifying.Correlation with proteinuria on the reagent strip helps in differentiating fatty cast from artefacts as there is damage to the glomerular membrane allows passage of both protein and lipids into the urinary filtrate
Clinical significance of fatty casts: Seen in Nephrotic syndrome, lipiduria, tubulointerstitial disorders
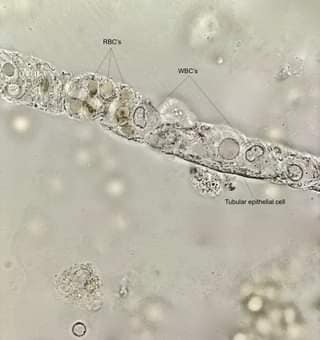
Mixed urinary casts: Cast matrix with mixed RBC,WBC,epithelial cells .seen in proliferative glomerulonephritis,tubulointerstitial diseases
| Urinary Cast Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Hyaline Cast | Transparent Acellular, clear matrix Smooth surface Low refractive index and colorless cylindrical casts composed mainly of Tamm-Horsfall protein. They are considered normal if present in small numbers. |
| Granular Cast | Contains fine or coarse granules derived from degenerated cellular elements or precipitated protein. They are usually associated with renal diseases and can indicate tubular damage. |
| Red Blood Cell Cast | Contains clumped RBCs and indicates glomerular bleeding, often associated with glomerulonephritis or vasculitis. |
| White Blood Cell Cast | Contains clumped WBCs and indicates inflammation within the kidney, such as pyelonephritis or interstitial nephritis. |
| Epithelial Cast | Contains renal tubular epithelial cells shed from damaged tubules. It suggests tubular injury or acute tubular necrosis. |
| Waxy Cast | Broad, highly refractive casts with smooth edges. They indicate stasis or stenosis within the renal tubules and are associated with chronic renal failure. |
| Fatty Cast | Contains fat globules and is seen in conditions like nephrotic syndrome, where lipid metabolism is altered. |
| Broad Cast | Broad casts that often contain cellular debris and may indicate severe tubular injury or chronic renal disease. |
| Cylindroid Cast | Elongated and often twisted casts, similar to hyaline casts but larger. They can be seen in various renal diseases. |
| Pigmented Cast | Contains granules of pigments such as hemoglobin or myoglobin and indicates hematuria or rhabdomyolysis. |

Useful… Effective content👍