Blood ammonia level test measures the amount of ammonia in the blood. Ammonia is a waste product produced by the body during the breakdown of proteins and is normally processed by the liver.
The test is often used to evaluate the function of the liver, as the liver is responsible for converting ammonia into a less toxic substance called urea. Elevated ammonia levels may indicate liver dysfunction.
Indications of ammonia testing
Ammonia is used to support the diagnosis of severe liver diseases like fulminant hepatitis , cirrhosis. Ammonia levels are also used in the diagnosis and follow-up of hepatic encephalopathy.
Inherited deficiencies in urea cycle enzymes, metabolic disorders involving organic acids, and disruptions in the metabolism of dibasic amino acids like lysine and ornithine are significant contributors to elevated ammonia levels in both infants and adults.Impaired renal function can lead to reduced ammonia excretion, resulting in elevated blood levels
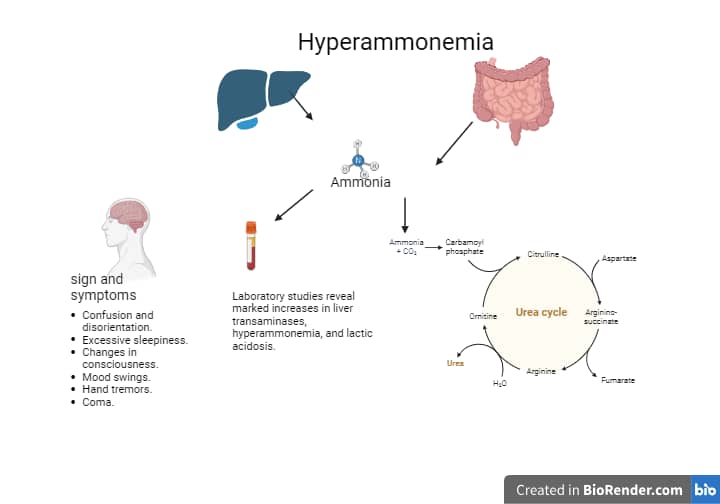
causes of hyperammonemia(raised level of ammonia)
Primary hepatocellular disease ,Reye syndrome ,Asparagine intoxication ,Portal hypertension ,Severe heart failure with congestive hepatomegaly, Hemolytic disease of the newborn (erythroblastosis fetalis),Gastrointestinal bleeding ,Gastrointestinal obstruction with mild liver disease, Hepatic encephalopathy and hepatic coma ,Genetic metabolic disorder of the urea cycle.
Therapy with valproate is associated with hyperammonemia.
Preanalytical factors in ammonia level testing
Given the significance of this biochemical marker and the potential repercussions of false positive results on a patient’s diagnosis and treatment, it is crucial to exercise caution in order to minimize artifacts arising from pre-analytical factors.
- Patient preparation : If not a emergency sample is preferred in fasting state. Cigarette smoking can produce significant increases in levels smoking should be avoided for at least 9 hours before the sample is collected ,physical Exercise should be avoided before collection. Donors arms should be as relaxed as possible, because muscle exertion may increase venous ammonia levels. Ammonia levels may be falsely increased if the tourniquet is too tight for a long period ,tourniquet should not be applied for more than 1 minute. Drugs that may cause increased ammonia levels include acetazolamide, alcohol, ammonium chloride, barbiturates, diuretics (e.g., loop, thiazide), narcotics, and parenteral nutrition
2. Sample Collection and transportation : Plasma ammonia concentration is also affected by the venipuncture technique and the temperature of the sample . A consensus statement from the Urea Cycle Disorders Conference Group recommends collecting free flowing venous or arterial blood in a pre-chilled EDTA or Heparin tube , ensuring it is kept on ice, and promptly delivering it to the laboratory 2.
3. Plasma separation : Plasma separation should be performed within 15 minutes of collection. Once separated, ammonia is stable for 4 h at 4 °C and 24 h at -20 °C.
Rejection criteria :
Hemolysed sample.
Clotted samples
samples collected via indwelling catheters and capillary samples.
Methodology -Bromophenol blue diffusion in dry chemistry, enzymatic .
Reference range of plasma ammonia – Reference interval (adults): 11–32 µmol/L
premature neonates, <150 µmol/L; term neonates, <100 µmol/L; infants <40 µmol/L.
References
1.Robert J Barsotti PhD ,Measurement of ammonia in blood
2. Proceedings of a Consensus Conference for the Management of Patients with Urea Cycle Disorders Marshall Summar, MD, and Mendel Tuchman, MD
3. Ibrahim A. Hashim, Jennifer A. Cuthbert,
Elevated ammonia concentrations: Potential for pre-analytical and analytical contributing factors,
Clinical Biochemistry, Volume 47, Issues 16–17,2014,Pages 233-236,ISSN 00099120,https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clinbiochem.2014.08.013.
(https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0009912014006481)
