Introduction
The nitrite test in urine is a quick, cost-effective, and indirect method used to detect significant bacteriuria. This test provides a valuable and relatively efficient way to screen for the presence of bacteria in the urinary tract, which can indicate a potential urinary tract infection (UTI) , specifically those caused by Nitrate reducing bacteria.
Nitrite test in urine comes positive when these bacteria are in significant number usually around 105 -106 colony-forming units per milliliter.
Some of the common nitrate-reducing bacteria that can cause urinary tract infections (UTIs) include:
- Escherichia coli (E. coli)
- Klebsiella pneumoniae:
- Proteus mirabilis:
- Enterobacter spp.:
- Citrobacter spp.
- Pseudomonas aeruginosae.
sample collection:
First morning clean voided midstream urine specimen is best for nitrite in urine test. Transport specimen at 2-8 degree temperature.
Random urine samples and urine from patients with draining cathether do not show good correlation between beween nitrite test and significant bacteriuria because minimum 4 hours bladder incubation is typically required for the infecting bacteria to convert urinary nitrate to nitrite.
Principle of nitrite test in urine
The principle of a nitrite test in urine routine analysis is based on the ability of certain bacteria, specifically Gram-negative bacteria like Escherichia coli (E. coli), to convert nitrate (NO3-) present in the urine into nitrite (NO2-). This conversion occurs through a biochemical process known as nitrate reduction.
P-arsanilic acid present on multistix reacts with nitrite ions present in urine to form a diazonium salt. The diazonium salt formed in the first step then reacts with a reagent benzoquinoline to produce a pink colored azo dye. This method detects 0.075mg of nitrite per deciliter in urine.1
The intensity of the color change is proportional to the concentration of nitrite ions in the urine sample.
Procedure of urine nitrite test in urine
- Collection of Urine Sample: A midstream urine sample is collected from the patient. It is essential to ensure that the sample is collected in a clean container to prevent contamination.
- Dipstick Test: A nitrite test is often performed using a urine dipstick(multistix). The dipstick is a narrow strip of paper or plastic with several chemical pads or reagent areas.
- Dipstick Immersion: Dip the multistix strip into the urine sample according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Ensure that the strip is evenly wetted and allow it to react for the specified time.
- Chemical Reaction: If there are bacteria in the urine that can convert nitrates (a common component of urine) into nitrites, a chemical reaction will occur on the dipstick. This reaction usually involves a color change.
- Reading the Results: The technician observes the dipstick for any color change in the nitrite section. Reading should be observed at specified time as per manufacturer.
Interpretation:
positive nitrite test should be followed by urinary culture provided that urine collected and stored properly prior to testing.
A positive nitrite test result, along with other clinical symptoms and findings, may prompt further investigation and potentially the prescription of antibiotics to treat the urinary tract infection.
Urinary sample positive with nitrite and leukocyte esterase should be sent for bacterial culture.
The nitrite test is highly sensitive in detecting urinary tract infections (UTIs), but it lacks specificity because not all bacteria in the urinary tract can convert nitrates to nitrites. Bacteria such as Staphylococcus, Streptococcus, and Haemophilus do not possess this nitrate-reducing ability. Therefore, a negative nitrite test result does not definitively rule out the presence of bacteria in the urinary tract, including potential UTI-causing pathogens.
A negative result should not exclude the possibility of a UTI.
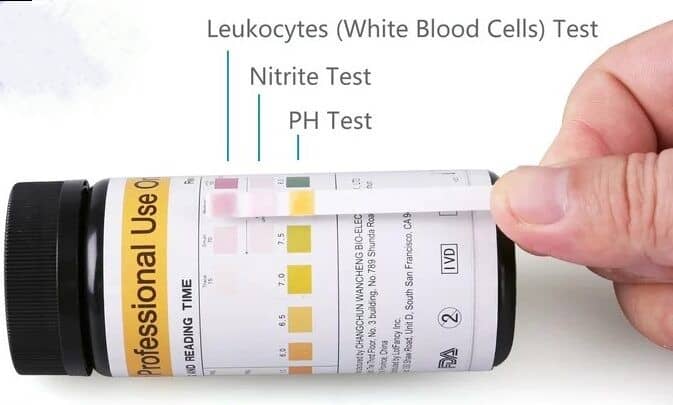
Limitations of urine nitrite test
| causes of false Positive nitrite test | causes of false Negative nitrite test |
|---|---|
| Contamination of the urine sample during collection or handling (post collection contaminant bacterial proliferation) | low pH less than 6 |
| Medications: Certain medications (e.g., phenazopyridine) can cause a temporary increase in nitrite levels | lack of dietary nitrate in urine |
| Azo dye metabolites and bilirubin can produce false positive results2 | Interference from substances in the urine ascorbic acid ,urobilinogen |
| error in reading results | error in reading results |
Reference
1.Henry’s clinical diagnosis and management by laboratory methods 23rd edition
2. Fischbach’s manual of Laboratory and diagnostics test, page no.218 11th edition
C-peptide testing
What is C-peptide? C peptide originates in pancreatic beta cells as a byproduct of enzymatic cleavag…
sickling test |Sickling test procedure
Introduction : Sickle cell disease is an inherited hemoglobin disorder caused by a mutation in the …
Pus cells in urine microscopy
The presence of pus cells in the urine, also known as pyuria, is a sign of infection and inflammatio…
Reticulocyte count – procedure, corrected reticulocyte count
Contents hide 1 Why Is Reticulocyte Count Important? 2 Principle of reticulocyte staining: 2.1 Prepa…
How to perform CSF Examination- Detailed procedure for Physical, chemical,cell counts
Contents hide 1 What is CSF? 1.1 TEST PROCEDURE: 1.2 Physical examination of CSF 1.2.1 Differential …
cardiac troponins -Troponin I ,Troponin T TEST
The cardiac biomarker that is preferred for diagnosis of Acute Myocardial Infarction is troponin, wh…
streamline your clinical lab work
At clinical laboratory guide, we are passionate about simplifying clinical lab work. Our blog provid…
HOW TO CALCULATE e-GFR
Serum eGFR (estimated Glomerular Filtration Rate) is commonly calculated using the CKD-EPI (Chronic …
Hansel’s Stain for Detection of Urinary Eosinophils
Contents hide 1 Purpose 2 Preparation of Hansel’s Stain Solution (if preparing manually) 2.1 1. Eosi…
Formula for citrate volume adjustment In high hematocrit
When collecting blood into a citrate bulb (commonly used for coagulation tests like PT, APTT, etc.),…
H pylori antigen stool vs H pylori antibody in serum which one is better?
Contents hide 1 H. pylori Stool Antigen Test 2 H. pylori Antibody Test (Serology) 3 Which one is bet…