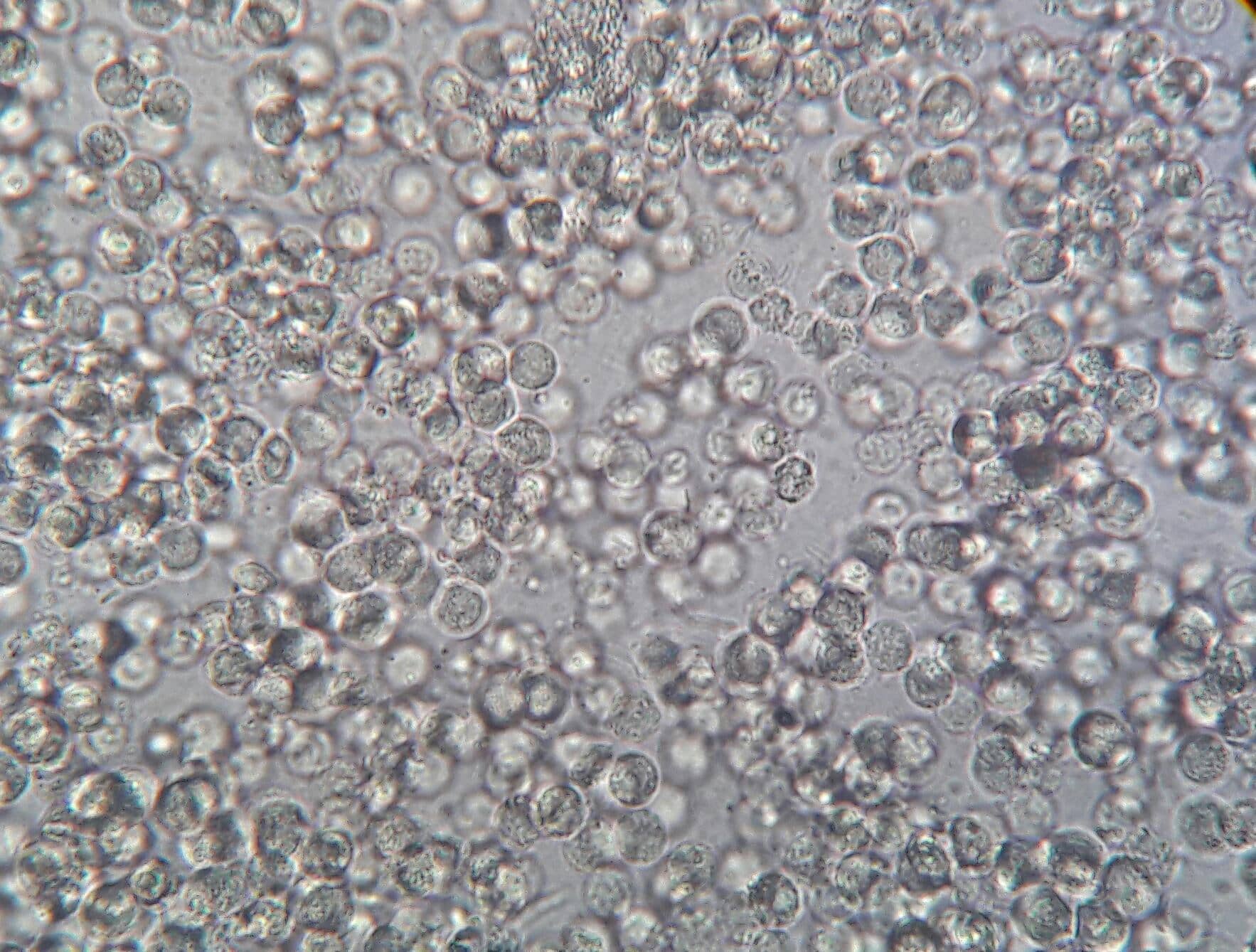
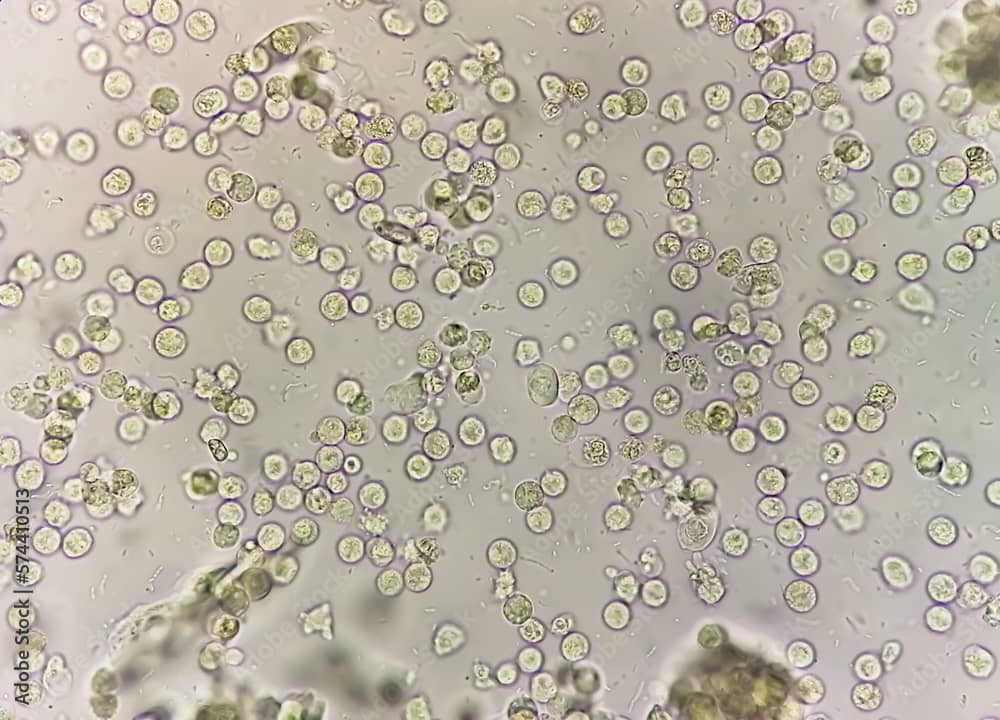
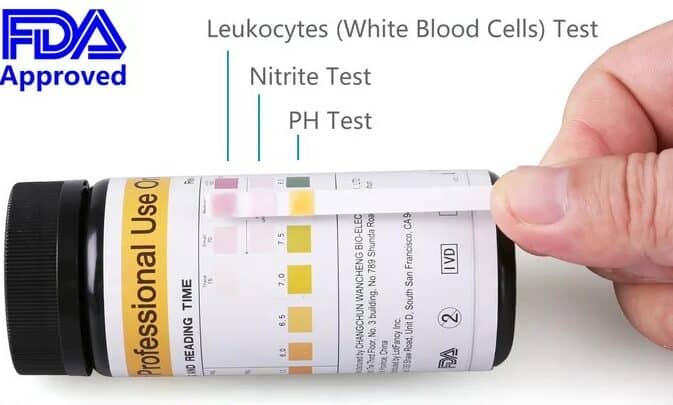
The presence of pus cells in the urine, also known as pyuria, is a sign of infection and inflammation in the urogenital system. Pus cells refers to presence of leukocytes in urine .It is produced by the body’s immune system to fight infection.
what is normal range of pus cells in urine?
A normal urine sample will have 0 – 5 WBC’s per HPF. Women may have slightly higher count of pus cells.
Leucocytes in unstained urine sediments typically appear as round and granular. Neutrophils are the most common type of WBC found in urine .The details of nuclear shape often are difficult to discern due to degenerative changes .The supra vital stain facilitates identification of the aids in the differentiation of polymorphonuclear leucocytes from lymphocytes, histiocytes, plasma cells, and renal tubular cells.
what are glitter cells in urine?
Glitter cells are also known as Sternheimer-Malbin cells, are polymorphonuclear leukocytes (PMNs) with their granules showing Brownian movement when viewed under a microscope. They are typically found in urine with a low specific gravity (hypotonic urine). these cells stain poorly with supravital stain, leucocyte esterase positive dipstick helps in confirmation of pyuria in such cases
Also note leucocytes are rapidly lysed in hypotonic and alkaline urine , approximately 50% leucocytes are lost in 2-3 hours ,if sample kept at room temperature.
What is significance of Eosinophils in urine?
Eosinophil is suggestive of interstitial nephritis and drug-induced nephritis. Eosinophils are better demonstrated by Hansel’s stain. Few eosinophils may be seen in urinary tract infections and renal transplantation rejection. The percentage of >1% eosinophils in urine is significant.
What is significance of lymphocytes in urine?
small lymphocytes are normally present in urine . Raised lymphocyte count in urine is seen in renal transplant rejection, lupus nephritis.
More than 30% Macrophages and plasma cells in urine signify chronic inflammation.
Conditions that can cause pyuria, including:
- Urinary tract infection (UTI): This is the most common cause of pyuria. UTIs can be caused by bacteria, viruses, or fungi. most common cause of UTI is E. coli bacterial infection
- Prostatitis
- Kidney stones
- Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID)
- Sexually transmitted infections (STIs): Some STIs, such as gonorrhea and chlamydia, can cause pyuria.
- Autoimmune disorders : Autoimmune diseases, such as lupus and rheumatoid arthritis can cause inflammation and pyuria
symptoms
- Painful urination
- Frequent urination
- Burning sensation during urination
- Cloudy or bloody urine
- Fever
- Chills
- Nausea
- Vomiting
what is sterile pyuria?
Sterile pyuria is the persistent finding of white cells in the urine in the absence of bacteria, as determined by means of aerobic laboratory techniques
Renal tract tuberculosis
Chlamydial infection
Interstitial nephritis
Recent treatment of UTI with antibiotics
Renal papillary necrosis
lupus nephritis
Gonorrhea infection
Reference –
Henry clinical diagnosis and management by laboratory methods
https://www.nejm.org/doi/full/10.1056/NEJMra1410052
C-peptide testing
What is C-peptide? C peptide originates in pancreatic beta cells as a byproduct of enzymatic cleavag…
sickling test |Sickling test procedure
Introduction : Sickle cell disease is an inherited hemoglobin disorder caused by a mutation in the …
Pus cells in urine microscopy
The presence of pus cells in the urine, also known as pyuria, is a sign of infection and inflammatio…
Reticulocyte count – procedure, corrected reticulocyte count
Contents hide 1 Why Is Reticulocyte Count Important? 2 Principle of reticulocyte staining: 2.1 Prepa…
How to perform CSF Examination- Detailed procedure for Physical, chemical,cell counts
Contents hide 1 What is CSF? 1.1 TEST PROCEDURE: 1.2 Physical examination of CSF 1.2.1 Differential …
cardiac troponins -Troponin I ,Troponin T TEST
The cardiac biomarker that is preferred for diagnosis of Acute Myocardial Infarction is troponin, wh…
streamline your clinical lab work
At clinical laboratory guide, we are passionate about simplifying clinical lab work. Our blog provid…
HOW TO CALCULATE e-GFR
Serum eGFR (estimated Glomerular Filtration Rate) is commonly calculated using the CKD-EPI (Chronic …
Hansel’s Stain for Detection of Urinary Eosinophils
Contents hide 1 Purpose 2 Preparation of Hansel’s Stain Solution (if preparing manually) 2.1 1. Eosi…
Formula for citrate volume adjustment In high hematocrit
When collecting blood into a citrate bulb (commonly used for coagulation tests like PT, APTT, etc.),…
H pylori antigen stool vs H pylori antibody in serum which one is better?
Contents hide 1 H. pylori Stool Antigen Test 2 H. pylori Antibody Test (Serology) 3 Which one is bet…



1 thought on “Pus cells in urine microscopy”